Menu 1
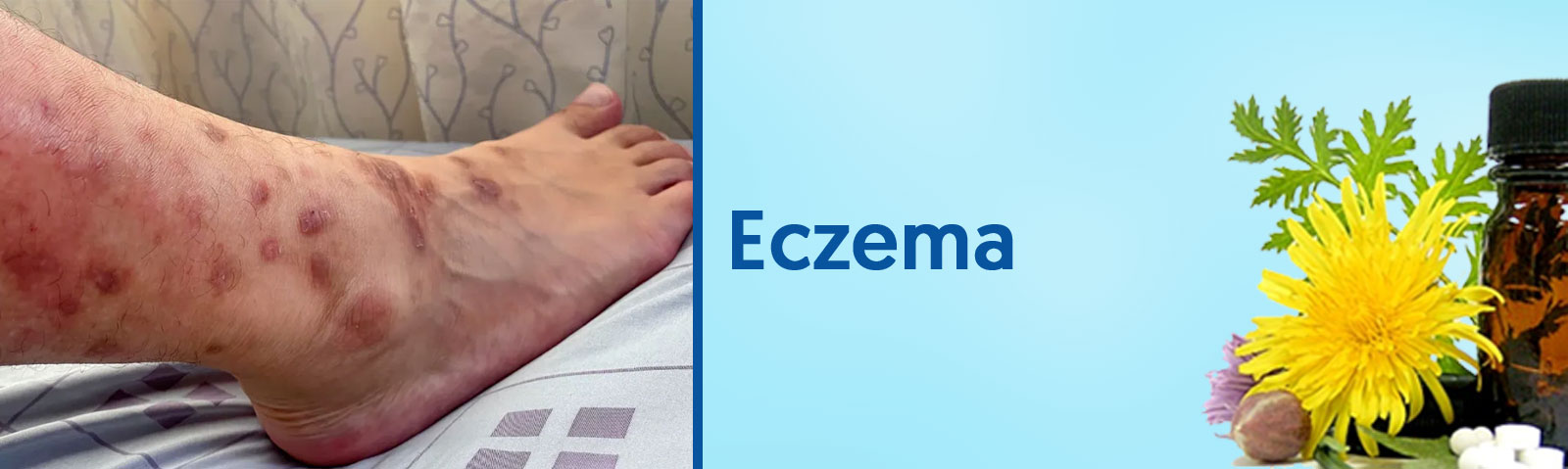
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that causes dry, itchy and inflamed skin. It's common in young children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare sometimes. It can be irritating but it's not contagious. People with atopic dermatitis are at risk of developing food allergies, hay fever and asthma
Symptoms:
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) symptoms can appear anywhere on the body and vary widely from person to person. They may include:
Atopic dermatitis often begins before age 5 and may continue into the teen and adult years. For some people, it flares and then clears up for a time, even for several years.
Causes:
In some people, atopic dermatitis is related to a gene variation that affects the skin's ability to provide protection. With a weak barrier function, the skin is less able to retain moisture and protect against bacteria, irritants, allergens and environmental factors such as tobacco smoke.
In other people, atopic dermatitis is caused by too much of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus on the skin. This displaces helpful bacteria and disrupts the skin's barrier function. A weak skin barrier function might also trigger an immune system response that causes the inflamed skin and other symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is one of several types of dermatitis. Other common types are contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). Dermatitis isn't contagious.
Risk factors:
The main risk factor for atopic dermatitis is having had eczema, allergies, hay fever or asthma in the past. Having family members with these conditions also increases your risk.
